Spotify may have changed the way we listen to music, but the various mobile carriers, especially in the United States and Canada, have been slow to adapt the plans they offer to accommodate the change.
While the rest of the world is increasingly moving towards unlimited data plans, data caps are still common. Why are there data limits and how can you bypass them? Why do data limits exist and how can they be bypassed? ISPs and mobile data caps are the bane of everyday Internet users. Why do these exist? Is there any way to get around them? This is what we know. Read More This has forced many people to think about the amount of data services like Spotify that are consumed each month. Let's take a closer look.
The amount of data Spotify uses while streaming depends on the music quality settings you've chosen. There are three settings to choose from:Normal , High , and Extreme . You can change the setting by opening Spotify and going to Settings> Music Quality> Streaming .
In normal settings, a three-minute song will use approximately 2 MB of data. At High, that jumps to 3.5MB, and at Extreme it goes as high as 7.5MB.
Every hour, that translates to 40MB, 70MB, and 150MB, respectively.
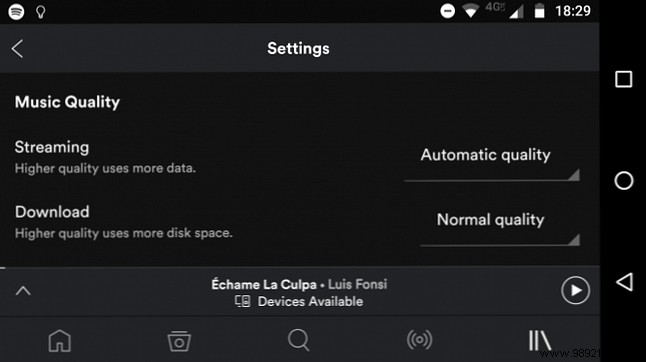
Extrapolating further from that data, if you listen to Spotify for an average of 30 minutes a day, you can use 0.5GB in a month on Normal and 2.2GB on Extreme. If you listen to an hour of streamed music, it increases to 1.2GB and 4.5GB. And if you listen for two hours, you'll need 2.4GB or 9GB respectively.
Lastly, it's worth noting that those figures are significantly easier to use than music via YouTube. An hour of music video streaming at the lowest video quality will still consume up to 100MB.
Remember, you can download Spotify songs for offline listening. You are limited to 3,333 songs per device on a maximum of three devices.
To download a song or playlist How to Download Spotify Songs for Offline Play How to Download Spotify Songs for Offline Play Spotify provides a way to download songs to your device so you can play them anytime, anywhere. Read More position.